Optimization fuel-consuming in platooning of vehicles by using sophisticated meta-heuristics
Abstract
Platooning of vehicles is a novel approach to reduce fuel consumption in long-distance transportation services by establishing a string of vehicles driving on the road close behind each other to reduce the aerodynamic drag. The motivation relies on the fact that the fuel costs are held accountable for the third of the total operational costs of those services, besides being the Heavy-duty vehicles one of the carbon emissions sources.
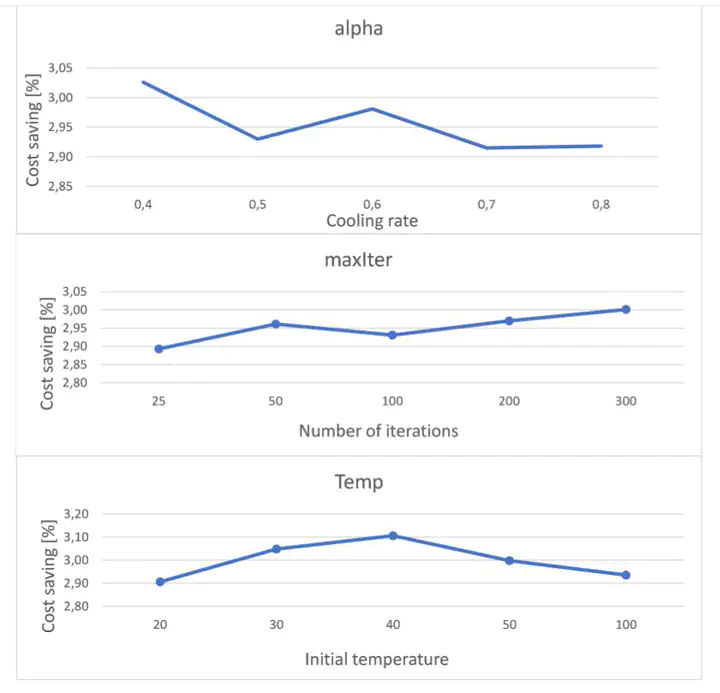
In this study, we examine the important but complex problem of assigning optimal routes to a set of vehicles, where many platooning potentials can be offered. We use the Simulated Annealing metaheuristic approach to solve the centralized routing problem with realistic assumptions on a real-world map. A robust design method is used to tune the model parameters. Unlike the previous contributions, a restriction on the platoon size is proposed to avoid traffic congestion. For a fair evaluation, a mathematical optimization solver using Gurobi is implemented based on a mathematical formulation of the problem. An additional sensitivity analysis is made to study the impact of different model parameters on the output.
In practice applying simulated annealing achieved approximately 5% fuel saving with an instance that has 500 trucks. For evaluating the algorithm on a real-live map the algorithm scored near 4.5% of fuel saving. The findings confirmed a satisfactory performance of the approach over the exact solver even when the restriction of the platoon size is applied, which can have a positive influence at the forefront of the platooning field, as solving the problem and enhance the solution in a reasonable time can ensure a globally optimized fuel cost-saving for the participants besides bringing environmental benefits.